Introduction
Sudan, a country already grappling with longstanding conflicts and instability, now faces a dire humanitarian crisis as famine threatens millions of its people. The escalating food insecurity has led to severe shortages, with a growing number of people in urgent need of assistance. This article examines the background and history of Sudan’s current crisis, the broader implications for its population, and the international community’s response to the urgent appeals for aid access.
Sudan’s humanitarian crisis is compounded by ongoing political instability and economic turmoil, which have severely impacted the country’s ability to respond effectively to the crisis. The combination of conflict, inadequate infrastructure, and economic collapse has exacerbated the suffering of millions, making the provision of aid and support even more challenging. In this context, understanding the broader implications and the international response is crucial to addressing the crisis and supporting the affected population.
Background: Sudan’s Complex History of Conflict and Instability
The Legacy of Conflict
Sudan has been plagued by conflict for decades, with its history marked by civil wars, internal strife, and political instability. The Sudanese Civil War (1983-2005) and the Darfur conflict (2003-present) are among the most notable, causing immense suffering and displacement. The 2011 secession of South Sudan, a result of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA), was intended to bring stability but instead led to further regional tensions and conflict.
The Fall of Omar al-Bashir
In April 2019, Sudan’s long-time dictator Omar al-Bashir was ousted after months of widespread protests against his regime. The transition to a civilian-led government, which began with a power-sharing agreement between the military and civilian factions, aimed to address the country’s political and economic challenges. However, this transition has been fraught with difficulties, including economic turmoil, ongoing conflict, and political instability.
The Current Famine Crisis
The Crisis Unfolds
The famine in Sudan has been exacerbated by a combination of factors, including prolonged conflict, economic mismanagement, and climatic challenges. The country’s agricultural sector, vital for food security, has been severely impacted by the conflict, leading to disrupted food production and distribution. Additionally, economic instability and inflation have eroded the purchasing power of millions, making it difficult for families to afford basic necessities.
Humanitarian Impact
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) has issued stark warnings about the deteriorating situation in Sudan. Jens Laerke, spokesperson for OCHA, has highlighted the severe consequences of the famine, stating that it is “likely to take hold in large parts of the country.” Laerke warned that the crisis would lead to increased displacement, worsening malnutrition, and heightened risks for women and girls.
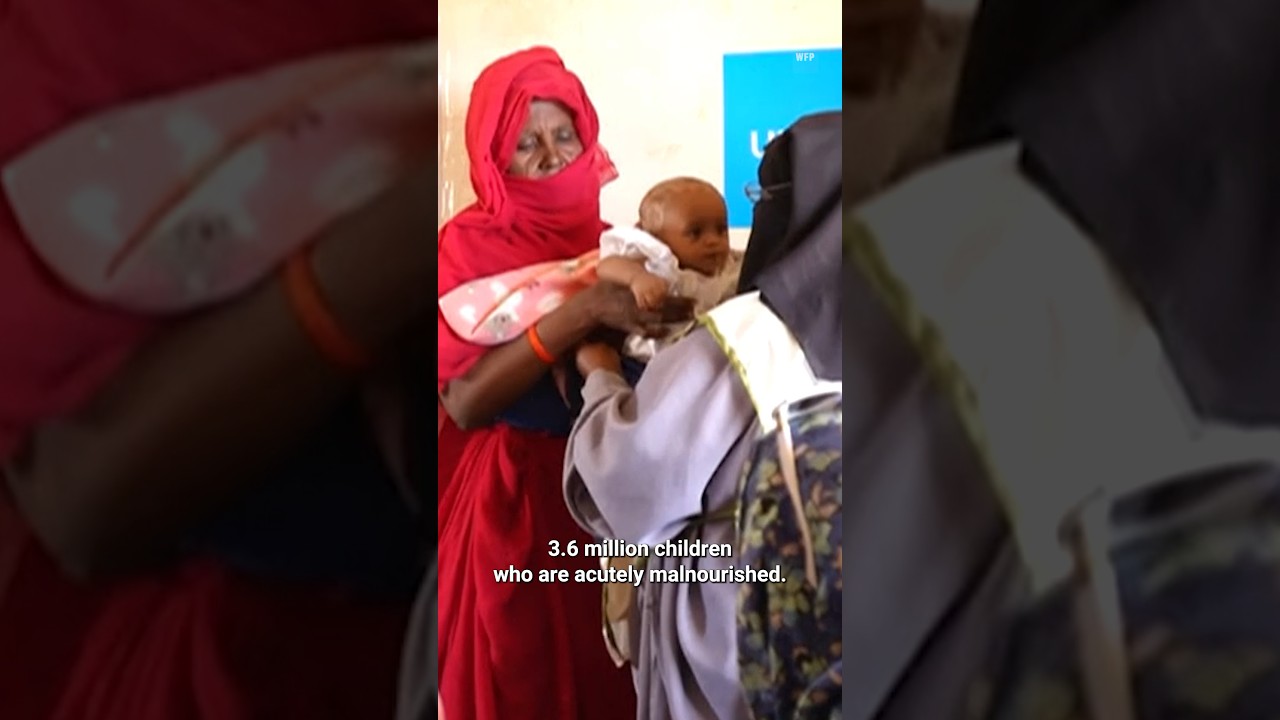
According to OCHA, millions of people are facing acute food insecurity, with many already experiencing extreme hunger. The lack of access to food and essential services has led to a surge in malnutrition rates, particularly among children. The situation is further compounded by the spread of diseases, which are exacerbated by the lack of adequate medical care and sanitation.
Broader Implications of the Famine Crisis
Regional Impact
The famine in Sudan has significant implications for the broader region. As the crisis intensifies, it is expected that more people will flee to neighboring countries in search of refuge and assistance. This influx of refugees can strain the resources and infrastructure of host countries, potentially leading to regional instability and humanitarian challenges.
Humanitarian Access and Aid
Access to affected areas is a critical issue in addressing the crisis. Humanitarian organizations face significant challenges in reaching those in need due to ongoing conflict, logistical difficulties, and restrictions imposed by various factions. Ensuring that aid reaches vulnerable populations is essential to mitigating the crisis and preventing further suffering.
The international community has called for greater access to affected areas and increased support for humanitarian operations. However, achieving these goals requires cooperation from all parties involved in the conflict and a commitment to allowing aid workers to operate safely and effectively.
International Response and Efforts
Humanitarian Appeals
The United Nations and various humanitarian organizations have made urgent appeals for increased funding and support to address the crisis. Efforts are focused on providing immediate relief, including food aid, medical assistance, and support for displaced populations. However, the scale of the crisis and the ongoing conflict pose significant challenges to delivering aid.
Diplomacy and Conflict Resolution
Addressing the underlying causes of the crisis requires diplomatic efforts and conflict resolution. The international community has called for renewed peace talks and negotiations to address the root causes of the conflict and promote stability in Sudan. The involvement of regional and international actors is crucial in facilitating dialogue and supporting peacebuilding initiatives.
Support for Development and Resilience
In addition to immediate relief efforts, there is a need for longer-term support to rebuild and strengthen Sudan’s resilience. This includes investing in agricultural development, infrastructure, and governance reforms to address the structural issues that contribute to the crisis. Supporting local communities and fostering economic opportunities can help reduce vulnerability and build resilience against future shocks.
The Role of the International Community
Collaborative Efforts
The international community plays a vital role in addressing the humanitarian crisis in Sudan. Collaborative efforts among governments, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are essential for providing comprehensive support and coordinating response efforts. The success of these efforts depends on effective collaboration, resource mobilization, and a commitment to addressing the needs of affected populations.
Advocacy and Awareness
Raising awareness about the crisis and advocating for increased support are critical components of the international response. Highlighting the plight of those affected and the urgency of the situation can mobilize public support and encourage governments and donors to increase their contributions to relief efforts.
Conclusion
The famine crisis in Sudan is a tragic consequence of prolonged conflict, economic instability, and climatic challenges. The situation has led to severe food insecurity, malnutrition, and increased suffering for millions of people. The warnings from the UN and humanitarian organizations underscore the urgent need for immediate relief, increased aid access, and long-term support for recovery and resilience.
As the international community responds to the crisis, it is essential to focus on both immediate needs and underlying issues. Addressing the root causes of the conflict, improving humanitarian access, and supporting development initiatives are crucial for creating a more stable and prosperous future for Sudan. The collaborative efforts of governments, international organizations, and local communities will be key to overcoming the current crisis and building a more resilient and equitable society for all.








